Zn Ground State Electron Configuration
Crystal Construction of Zinc
The solid land structure of Zinc is Simple Hexagonal.
The Crystal construction can be described in terms of its unit Cell. The unit Cells repeats itself in three dimensional space to form the structure.
Unit Jail cell Parameters
The unit of measurement jail cell is represented in terms of its lattice parameters, which are the lengths of the cell edges Lattice Constants (a, b and c)
| a | b | c |
|---|---|---|
| 266.49 pm | 266.49 pm | 494.68 pm |
and the angles between them Lattice Angles (blastoff, beta and gamma).
| blastoff | beta | gamma |
|---|---|---|
| π/2 | π/two | two π/3 |
The positions of the atoms inside the unit cell are described by the set up of atomic positions ( teni, yi, zi) measured from a reference lattice bespeak.
The symmetry properties of the crystal are described past the concept of infinite groups. All possible symmetric arrangements of particles in three-dimensional space are described past the 230 space groups (219 distinct types, or 230 if chiral copies are considered distinct.
Zinc Diminutive and Orbital Properties
Zinc atoms accept thirty electrons and the electronic shell construction is [ two, viii, 18, two ] with Atomic Term Symbol (Quantum Numbers) iDue south0.
Bohr Atomic Model of Zinc - Electrons per energy level

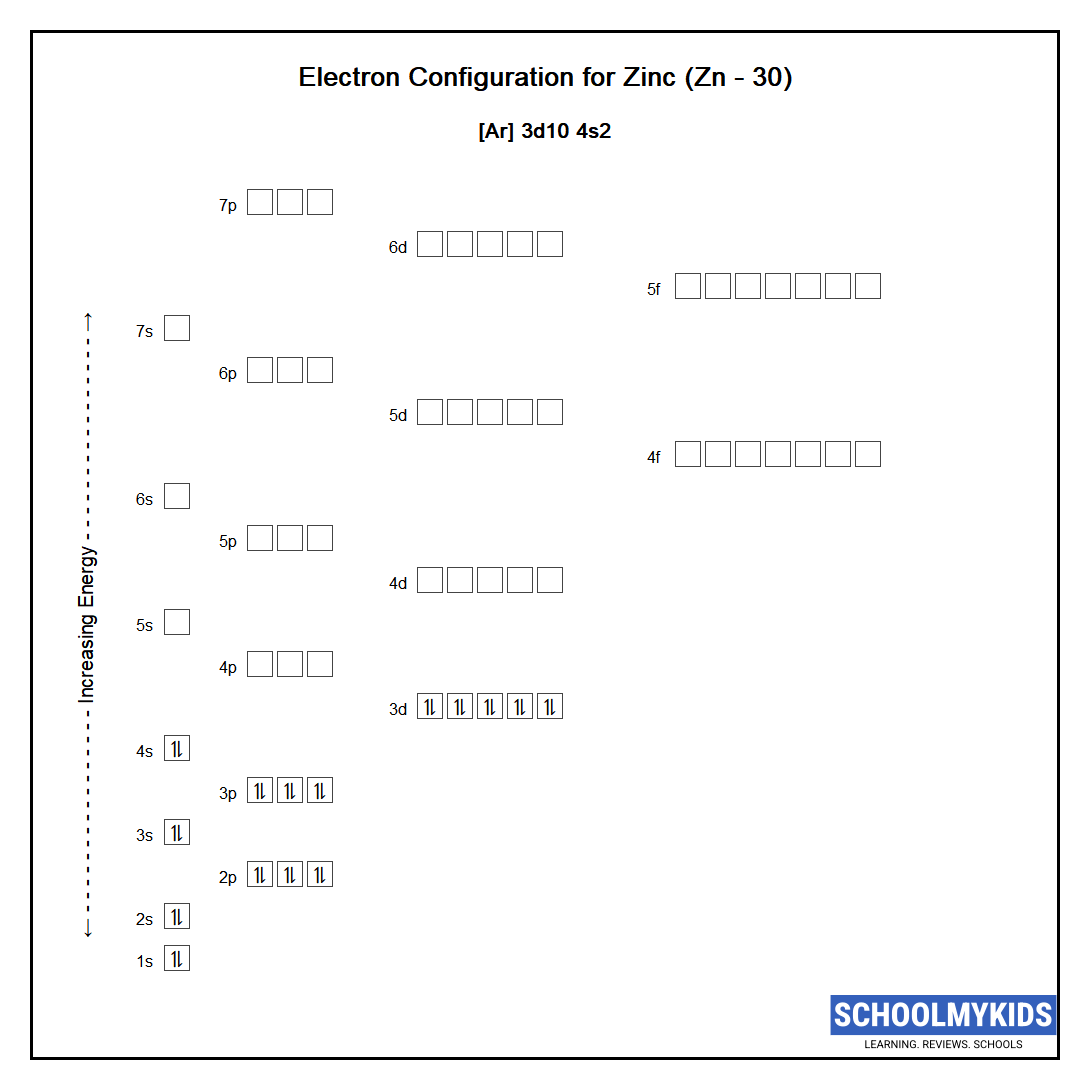
Ground State Electronic Configuration of Zinc - neutral Zinc atom
Abbreviated electronic configuration of Zinc
The ground land abbreviated electronic configuration of Neutral Zinc atom is [Ar] 3d10 4s2 . The portion of Zinc configuration that is equivalent to the noble gas of the preceding menses, is abbreviated every bit [Ar] . For atoms with many electrons, this notation can become lengthy and so an abbreviated notation is used. This is important equally it is the Valence electrons 3d10 4s2 , electrons in the outermost shell that determine the chemic properties of the element.
Unabbreviated electronic configuration of neutral Zinc
Complete footing country electronic configuration for the Zinc atom, Unabbreviated electronic configuration
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2
Electrons are filled in atomic orbitals as per the lodge determined past the Aufbau principle, Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund'due south Dominion.
Atomic Structure of Zinc
Zinc diminutive radius is 142 pm , while it'due south covalent radius is 131 pm .
| Atomic Radius Calculated | 142 pm ( i.42 Å) |
| Atomic Radius Empirical | 135 pm ( 1.35 Å) |
| Diminutive Volume | 9.161 cm3/mol |
| Covalent Radius | 131 pm ( 1.31 Å) |
| Van der Waals Radius | 139 pm |
| Neutron Cantankerous Section | 1.1 |
| Neutron Mass Absorption | 0.00055 |
Atomic Spectrum of Zinc
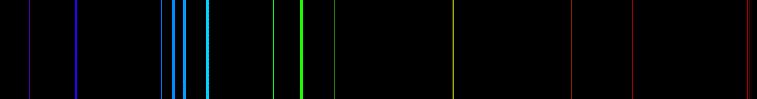
Zinc Chemic Properties: Zinc Ionization Energies and electron analogousness
The electron analogousness of Zinc is 0 kJ/mol .
Ionization Energy of Zinc
Refer to table below for Ionization energies of Zinc
| Ionization energy number | Enthalpy - kJ/mol |
|---|---|
| 1st | 906.4 |
| second | 1733.iii |
| third | 3833 |
| 4th | 5731 |
| 5th | 7970 |
| 6th | 10400 |
| 7th | 12900 |
| 8th | 16800 |
| ninth | 19600 |
| tenth | 23000 |
| 11th | 26400 |
| 12th | 29990 |
| 13th | 40490 |
| 14th | 43800 |
| 15th | 47300 |
| 16th | 52300 |
| 17th | 55900 |
| 18th | 59700 |
| 19th | 67300 |
| 20th | 71200 |
| 21st | 179100 |
Zinc Physical Properties
Refer to below tabular array for Zinc Physical Properties
| Density | vii.14 thou/cm3 (when liquid at m.p density is $ 6.57 one thousand/cm3 ) |
| Tooth Volume | 9.161 cm3/mol |
Rubberband Properties
Hardness of Zinc - Tests to Measure of Hardness of Element
Zinc Electric Properties
Zinc is Conductor of electricity. Refer to table below for the Electrical properties of Zinc
Zinc Heat and Conduction Backdrop
Zinc Magnetic Properties
Optical Properties of Zinc
Audio-visual Properties of Zinc
Zinc Thermal Properties - Enthalpies and thermodynamics
Refer to table beneath for Thermal properties of Zinc
Enthalpies of Zinc
Zinc Isotopes - Nuclear Properties of Zinc
Zinc has 30 isotopes, with betwixt 54 and 83 nucleons. Zinc has 5 stable naturally occuring isotopes.
Isotopes of Zinc - Naturally occurring stable Isotopes: 64Zn, 66Zn, 67Zn, 68Zn, 70Zn .
| Isotope | Z | Northward | Isotope Mass | % Abundance | T half | Decay Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 54Zn | thirty | 24 | 54 | Synthetic | ||
| 55Zn | thirty | 25 | 55 | Constructed | ||
| 56Zn | 30 | 26 | 56 | Constructed | ||
| 57Zn | 30 | 27 | 57 | Synthetic | ||
| 58Zn | 30 | 28 | 58 | Constructed | ||
| 59Zn | 30 | 29 | 59 | Synthetic | ||
| 60Zn | 30 | 30 | 60 | Synthetic | ||
| 61Zn | 30 | 31 | 61 | Synthetic | ||
| 62Zn | 30 | 32 | 62 | Synthetic | ||
| 63Zn | 30 | 33 | 63 | Synthetic | ||
| 64Zn | 30 | 34 | 64 | 48.63% | Stable | N/A |
| 65Zn | 30 | 35 | 65 | Synthetic | Stable | |
| 66Zn | 30 | 36 | 66 | 27.9% | Stable | N/A |
| 67Zn | thirty | 37 | 67 | four.1% | Stable | Due north/A |
| 68Zn | 30 | 38 | 68 | xviii.75% | Stable | Northward/A |
| 69Zn | thirty | 39 | 69 | Synthetic | ||
| 70Zn | 30 | 40 | 70 | 0.62% | Stable | N/A |
| 71Zn | 30 | 41 | 71 | Constructed | ||
| 72Zn | 30 | 42 | 72 | Constructed | ||
| 73Zn | 30 | 43 | 73 | Constructed | ||
| 74Zn | 30 | 44 | 74 | Synthetic | ||
| 75Zn | 30 | 45 | 75 | Constructed | ||
| 76Zn | 30 | 46 | 76 | Synthetic | ||
| 77Zn | 30 | 47 | 77 | Synthetic | ||
| 78Zn | 30 | 48 | 78 | Constructed | ||
| 79Zn | 30 | 49 | 79 | Constructed | ||
| 80Zn | 30 | 50 | 80 | Constructed | ||
| 81Zn | 30 | 51 | 81 | Synthetic | ||
| 82Zn | thirty | 52 | 82 | Constructed | ||
| 83Zn | 30 | 53 | 83 | Synthetic |
Zn Ground State Electron Configuration,
Source: https://www.schoolmykids.com/learn/periodic-table/zn-zinc
Posted by: bullhatuared.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Zn Ground State Electron Configuration"
Post a Comment